There are a variety of diodes out there, but in this post we will particularly stick with the Zener diode, LED and Photodiode. Here we will discuss mechanism, symbols, uses and the fundamental terms associated with these diodes. So let’s get into it.
Zener diode
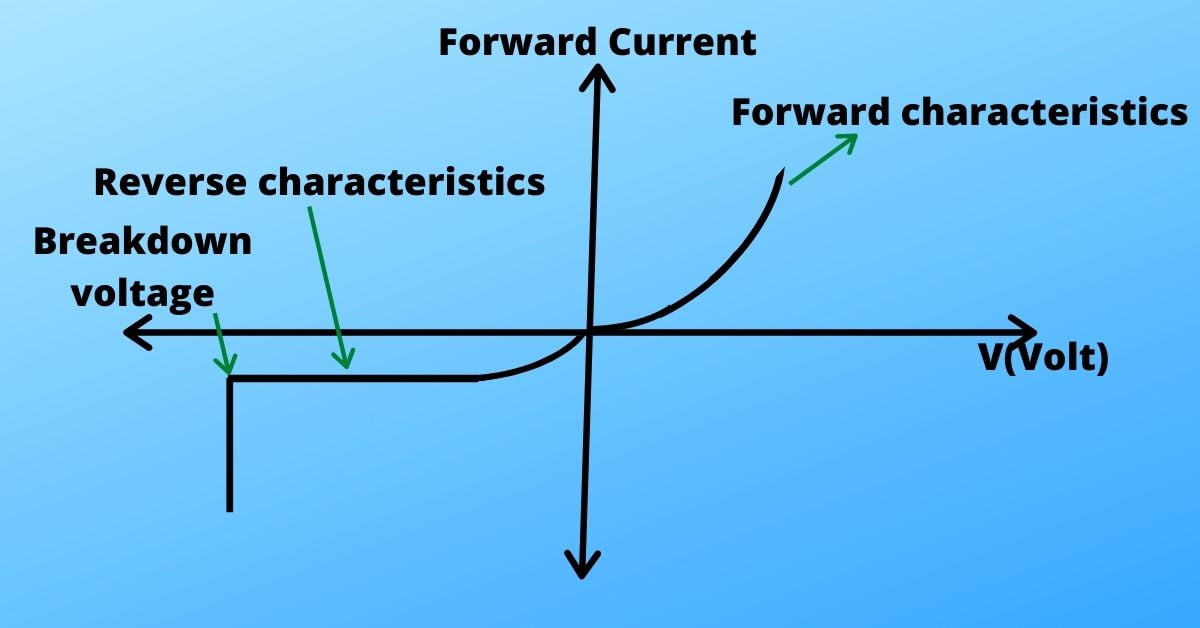
Zener diode is a highly doped p-n junction diode having a sharp breakdown voltage i.e. unlike normal p-n junction diodes, it conducts at a certain fixed reverse voltage.
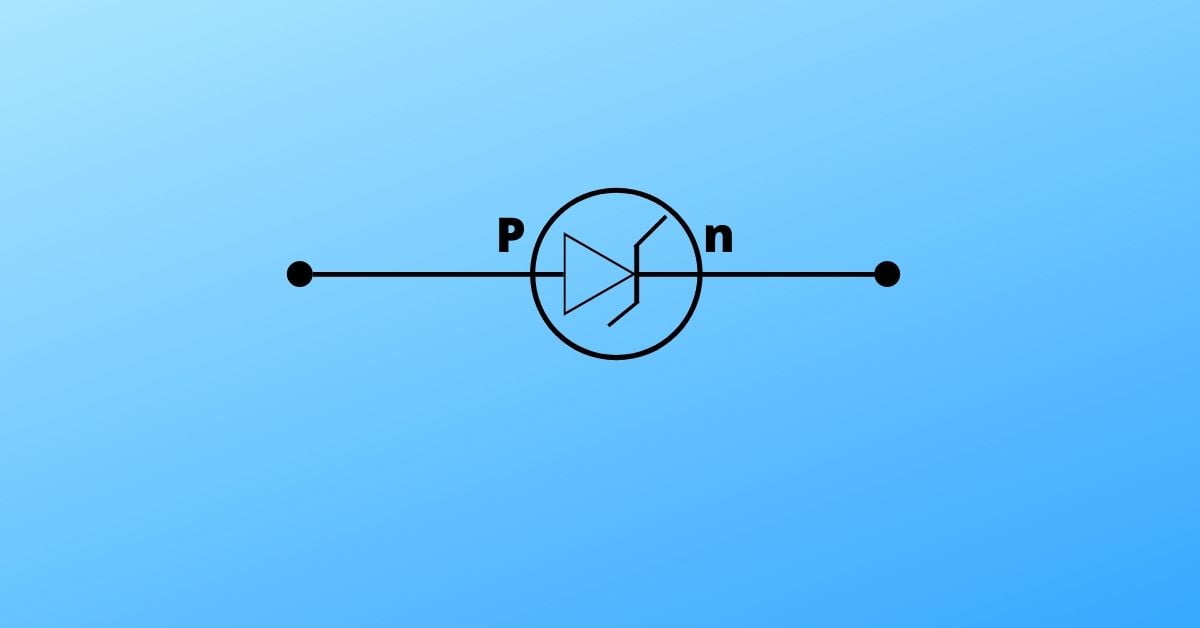
Circuit symbols
V-I characteristics
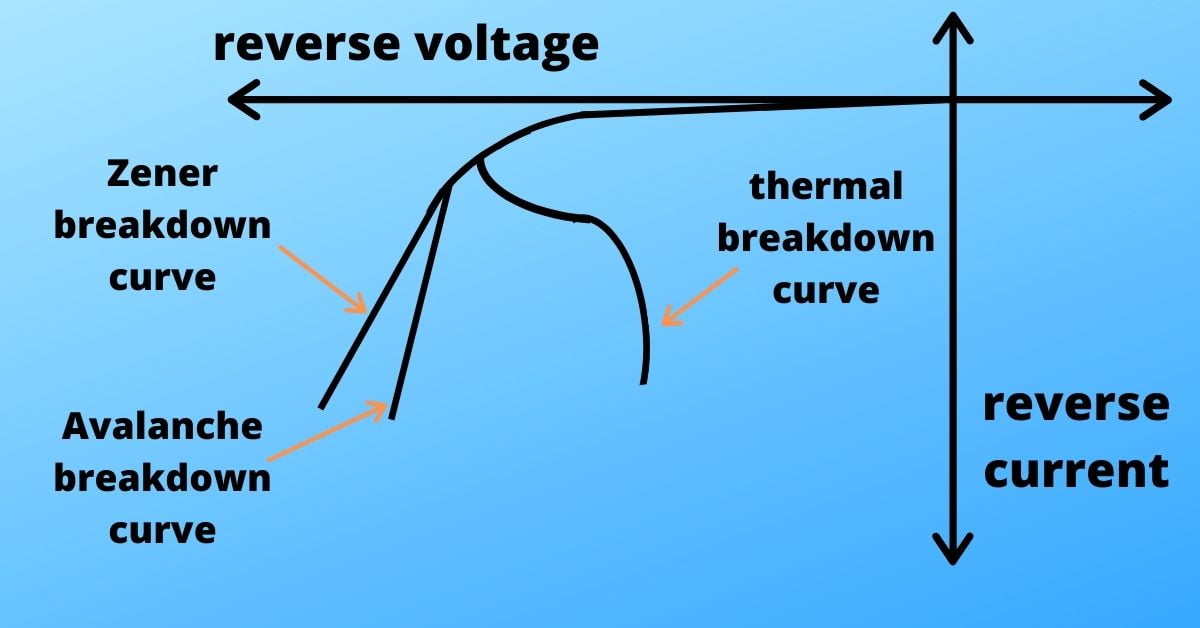
Breakdown Mechanisms
Avalanche Breakdown
When the applied reverse bias voltage across the p-n junction is small then we get a little current due to minority carriers. If we increase the reverse bias voltage further then we reach a certain point after which the applied field is so strong that the thermally generated charge carriers gain sufficient energy. When the charges start to flow through the junction they simply hit the immobile ions and break the covalent bond due to their high energy. This broken covalent bond produces a new electron-hole pair. The new carriers again gain sufficient energy and produce a new electron-hole pair. This cumulative process is called Avalanche Breakdown.
Zener Breakdown
You can consider the Zener Breakdown as the higher version of Avalanche Breakdown. If you skip the comparatively slower growing ‘thermally generated charge carriers’ part, this is what you end up with. If the applied reverse voltage is so strong then it can directly break the covalent bond. As a result, it produces a huge number of electron-hole pairs in a fraction of seconds and increases the reverse bias current abruptly. This phenomenon is called Zener Breakdown.
Thermal Breakdown
This is another type of breakdown where the heat generated by the current flowing through the junction in reverse bias is greater than the heat dissipated by the junction. For this, the junction region heats up rapidly. If this process is left for a while, the junction will be destroyed by overheating. This phenomenon is called thermal breakdown and it is not only restricted to the Zener diode but also applicable to any other diode.
Comparison graph of thermal, Zener and avalanche breakdown
Use of Zener diode as a voltage regulator
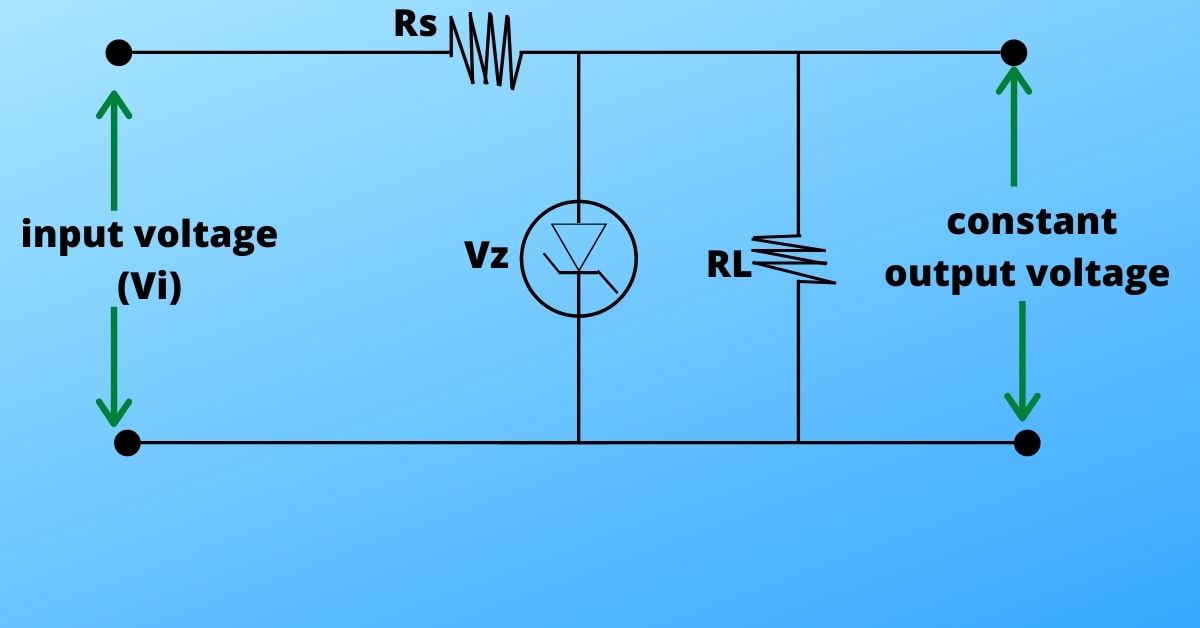
In the above circuit diagram we can see that a Zener diode having a Zener voltage,Vz is connected parallelly with the circuit. A series resistance, Rs is connected in series and another load resistance, RL is connected parallelly in the circuit. The input voltage source (input voltage, Vi) has to be connected with the Zener diode in reverse biased condition.
Case:1
When the circuit is closed, there is a fixed output voltage across the load. This fixed voltage is maintained until the input voltage is same/greater than the Zener voltage.
Case:2
When the input voltage is same/greater than Zener voltage, the Zener diode reverse-biased characteristics start to reflect. At the Zener voltage current will flow through the Zener diode as well as resistance Rs. Thus, to maintain the output voltage drop across Rs will also increase.
Other uses
As we have discussed, Zener diodes are used as voltage regulators. Other uses of Zener diodes are-
- Surge protector
- In clipping circuits
- In voltage shifter.
Light Emitting Diode (LED)
LEDs are one of the most common household devices that are used in our day to day applications. LEDs are small in size and they have high stability, longer life and low power consumption compared to the conventional ones.
Circuit symbol
Mechanism
Working principle of LEDs is a great example of conservation of momentum. When an electron and hole having exactly equal and opposite momentum recombines together they emit light in the form of radiation. In the case of Si and Ge, the recombination takes place indirectly via ‘recombination centres‘. So the heat generated in this process heats up the device. Hence, Si and Ge are not used to make LEDs.
Instead of Si and Ge, some ‘direct gap semiconductors’ like Gallium Phosphide (GaP), Gallium Arsenide Phosphide (GaAsP), etc. are used. In this kind of semiconductors, the recombination takes place directly so the excess energy emits in the form of radiation. By the way, LEDs are always connected in a forward bias condition.
Different Colours of LEDs
There exist LEDs with different types of colours in the market. Colour of a LED basically depends on two things one is the forbidden energy gap of the crystal and another is the concentration of impurities.
| semiconductor material | formula | band gap(eV) | emitted light |
| Silicon Carbide, 3C-SiC | SiC | 2.3 | Yellow |
| Silicon Carbide, 6H-SiC | SiC | 3 | Blue |
| Gallium Phosphide | GaP | 2.26 | green |
| Gallium Arsenide Phosphide | GaAsP | – | Red/Yellow |
| Gallium Arsenide | GaAs | 1.43 | Infrared |
| Nitrogen doped Gallium Phosphide | N+GaP | – | Yelow-Green |
| Zinc Oxide doped Gallium Phosphide | ZnO+GaP | – | Red |
Uses
LEDs are used in
- Digital display systems
- CD PLAYERS
- Indicators of power line voltage
- Optic fibre communications.
Photodiode
A photodiode is a special type of photo (light) sensitive diode in which the reverse-biased current is modified by the incident light flux.
Circuit symbol
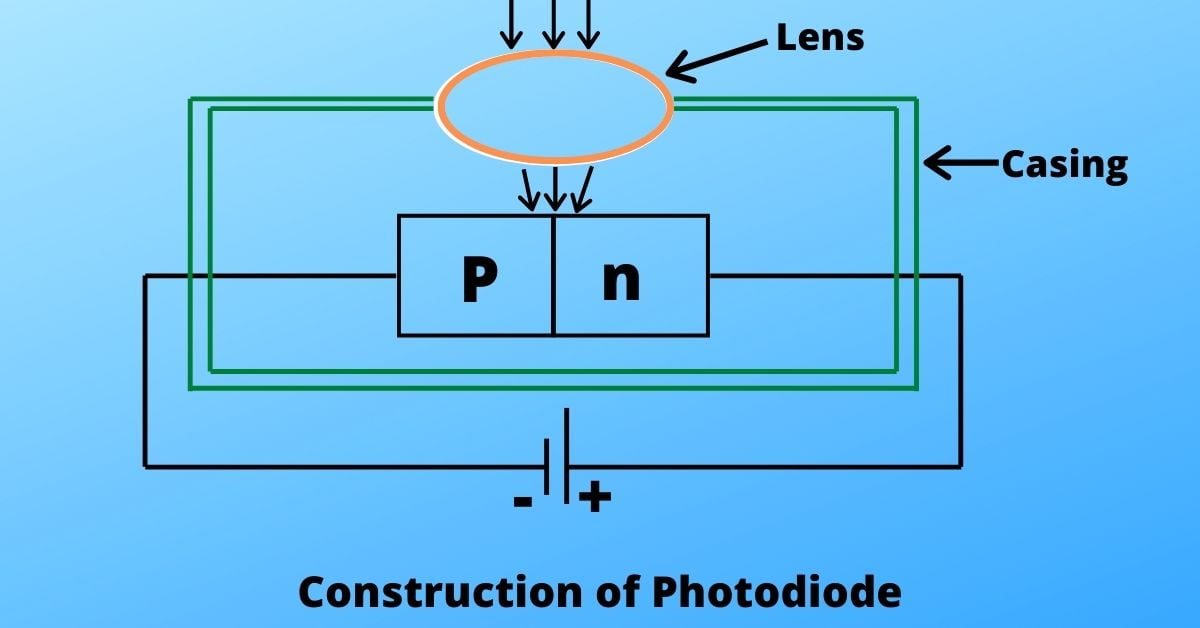
Mechanism
The Photodiode is generally covered within a casing. In this casing, a lens is placed from where the light will come. The reason behind this lens placing is to focus the light on the photodiode.
As we know, when a diode is kept in reverse bias condition, still a small amount current is flowing through the circuit due to the minority charge carriers. This current is called Reverse Biased Saturation current or dark current. Now, if a light beam falls on the photodiode the incident photons(light) disrupt the covalent bonds and produce new electron-hole pairs. This leads to an increase in the reverse saturation current. It has a linear dependence over the incident light intensity.
Types of Photodiode
There are four types of Photodiode-
- PN Photodiode
- PIN Photodiode
- Schottky Photodiode
- Avalanche Photodiode
Uses
Photodiodes are used in
- High-speed reading of tapes
- Light operated switches
- Conveyor belt to count items
- Light detection switches.
If you have any query regarding this post, please comment below. we will try our best to answer. Thank you.
What is a Zener Diode?
Zener diode is a highly doped p-n junction diode having a sharp breakdown voltage i.e. unlike normal p-n junction diodes, it conducts at a certain fixed reverse voltage.
What are the factors for determining the Colors Of LEDs?
Colour of a LED basically depends on two things one is the forbidden energy gap of the crystal and another is the concentration of impurities.
What is a Photodiode?
A photodiode is a special type of photo (light) sensitive diode in which the reverse-biased current is modified by the incident light flux.
What are the Uses of Zener Diode?
As Voltage Regulator, Surge protector, In clipping circuits, In voltage shifter.