Water is another name of life. Every living organism needs water to fulfil its biological needs and sustain its growth. But in the case of humans, the water we drink needs to be purified. This is because the surrounding environment may contaminate the water. It can happen through human interactions as well as by natural calamities. In both cases, water must be gone through a chain of purification processes before drinking. Let’s understand several contamination factors and their remedies that can help to provide safe drinking water in India.
Drinking water problem in India
According to UNICEF, every year almost an economic burden of 600 million dollars, the government needs to spend for waterborne diseases. Also, less than 50 per cent of Indians are fortunate to get safe drinking water. Besides the water crisis, getting safe water will be a challenge in the next few years. In drought-affected regions, the water crisis is a major problem.
In a 2017 report, NIUA said, almost 80 per cent of women including children were fetching water from outside. They are mostly taking the water of a public tubewell, pond, well, etc.

These sources are rarely tested for any water contaminations. Any waterborne disease caused by that contaminated water might be an outbreak in that area.
Cause of water Contaminations
There are several reasons behind water contaminations. Some of them are-
- Rapid urbanization
- Poor sewage treatment
- Excessive use of fertilizers
- Industrial chemical wastes dumping in rivers and seas
- Radioactive waste dumping
- Accidental oil leaks
The above points are the few man-made causes responsible for water contamination. Besides them, there are natural reasons too.
Arsenic contamination
According to WHO, Argentina, Bangladesh, Chile, China, India, Mexico, and the USA are among the few countries affected by high levels of arsenic contamination in groundwater. As of today, more than 70 countries are suffering from Arsenic contamination.
Arsenic (atomic number-33) is a highly toxic metalloid. Generally, arsenic is found in rock-solid compound forms in nature. Arsenic is present in the groundwater as “Oxy anions” having two oxidation states – Arsenite(+3), Arsenate(+5). Though the thermodynamic conditions preferred to have arsenate in Oxic water and arsenite in Anoxic water, they coexist in both types of waters. Studies also show that Arsenite is more toxic and harder to remove than Arsenate.
Excessive use of arsenic-based chemical products and their waste can be a possible cause of arsenic contamination. Apart from this, When the water level goes very low, the arsenic in rock form dissolves in groundwater naturally. This also causes water to be poisonous.
Side-effects:
Excessive levels of Arsenic can cause several health-related problems. Arsenicosis, a common name generally used for Arsenic related health problems including skin cancers, internal cancers, diseases of the blood vessels of the legs and feet, diabetes, high blood pressure, and reproductive disorders etc.
Fluoride Contamination
Fluorine(atomic number- 9) with another element or group is termed a Fluoride compound. In other words, salt of the anion Fluorine or an organic compound with fluorine bonded to an alkyl group is called Fluoride compound.
You can find it in your daily usage like in your toothpaste. It is well under the permissible limit. Above 10 mg/day for adults and 3 mg/day for children are considered as harmful. According to Indiawaterportal, 6 crore people of 100 districts in 20 states of India are consuming drinking water having fluoride levels more than 1 mg/l. This also causes health-related problems.
Side-effects:
Prolonged consumption of excessive levels of Fluoride can cause a disease namely Fluorosis. Fluorosis has two types-
- Skeletal fluorosis: It is a bone-related disease caused by a disturbance in our calcium metabolism. In skeletal fluorosis, the development of our bones is affected. Skeletal fluorosis weakens and softens our bones and eventually, it leads to crippling.
- Dental fluorosis: It is a tooth development-related disease generally found in children between 1 to 4 years age group. A high concentration of fluoride leads to porosity in teeth at an early age.
Rather than these two diseases, there are unhealthy and underweight newborn babies, shortage of Calcium in 40+ age people, pregnant and lactating women due to higher consumption of fluoride in pregnancy.
standards for drinking water in India
Serial No. | Parameters | Permissible Limit | Maximum Limit |
| 1. | Odor | Agreeable | Agreeable |
| 2. | Taste | Agreeable | Agreeable |
| 3. | PH | 6.5 – 8.5 | X |
| 4. | TDS (mg/l) | 500 | 2000 |
| 5. | Hardness (as CaCO3) (mg/l) | 200 | 600 |
| 6. | Alkalinity (as CaCO3) (mg/l) | 200 | 600 |
| 7. | Nitrate (mg/l) | 45 | x |
| 8. | Sulfate (mg/l) | 200 | 400 |
| 9. | Fluoride (mg/l) | 1 | 1.5 |
| Serial No. | Parameters | Permissible Limit | Maximum Limit |
| 10. | Chloride (mg/l) | 250 | 1000 |
| 11. | Turbidity (NTU) | 5 | 10 |
| 12. | Arsenic (mg/l) | 0.01 | 0.05 |
| 13. | Copper (mg/l) | 0.05 | 1.5 |
| 14. | Cadmium (mg/l) | 0.003 | x |
| 15. | Chromium (mg/l) | 0.05 | x |
| 16. | Lead (mg/l) | 0.01 | x |
| 17. | Iron (mg/l) | 0.3 | x |
| 18. | Zinc (mg/l) | 5 | 15 |
| 19. | Fecal Coliform (cfu) | 0 | 0 |
- Tds concentration: Total dissolved solids (TDS) is a measure of all inorganic and organic substances present in a liquid in molecular, ionized, or micro-granular (colloidal sol) suspended form. Generally, it has a range between 50 to 2000.
Possible solutions
Boiling and normal filtration are not enough for removing Arsenic and Fluoride from water. You need to have a purifier having RO, UF etc. in it. For normal filtration, ( not affected by Arsenic and Fluoride) you can use normal filters available in the market. Let’s see the technologies available for solving the above problems.
Types:
There are three types of purification processes generally used in all types of water purifiers. They are the RO (Reverse Osmosis) process, UV (Ultra-Violet) process and UF (Ultra-filtration) process.
RO (Reverse Osmosis) Process
RO process is the most effective technology for water purification to date. In RO technology, a pressure pump drives water through a membrane with very high pressure. The membrane has very tiny holes.
- How is the RO cylinder made?
Reverse osmosis membranes are made of a sheet, namely a membrane flat sheet. It consists of three main layers-a polyester fabric which supports the other two layers, a tiny porous poly cell phone layer and a 0.2-micron thick polyamide barrier layer. The barrier layer is responsible for removing the contaminants from the water. A spacer( feed channel spacer) is in between the flat sheet membranes to provide turbulence and also to create a path through the membrane sheets for the feed water.
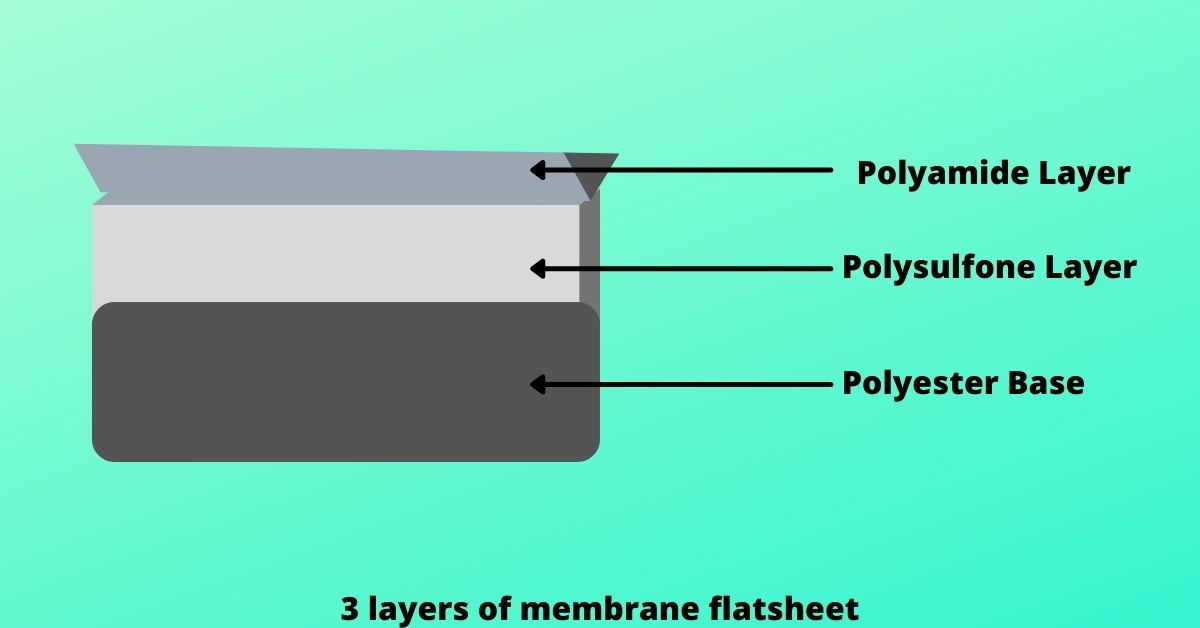
A sheet of permeate spacer is there to enable the water to flow evenly across the entire membrane surface even under high pressure. The backside of the membrane is completely blocked up to the edges of the spacer(permeate spacer).
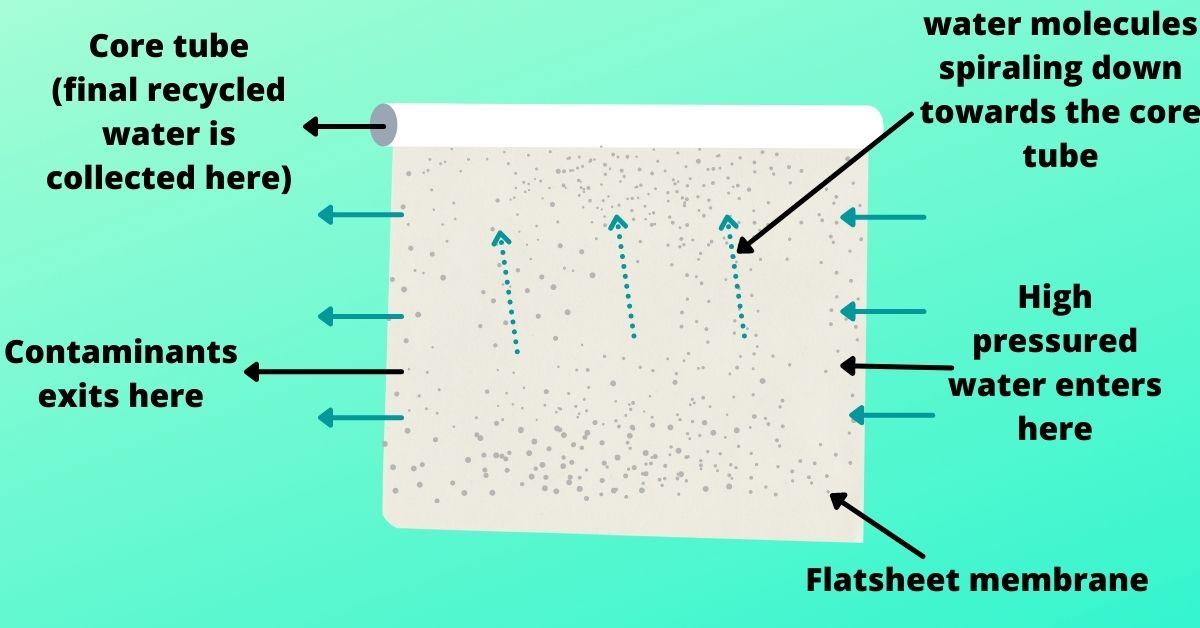
Each of the three exposed sides is glued to the membranes. The whole system then rolled around the core tube to collect the water within the tube. Water is forced to pass through the feed spacer and into the barrier layer. The direction of water flow is from the membrane surface towards the permeate channel which makes a spiral flow and collects in the core tube. This water is RO technology-based recycled water.
UF( Ultrafiltration) technology
UF technology is the most simple and effective way to purify water. It is membrane-based filtration technology in which the water pressure leads to the separation of water molecules and pollutants through a semipermeable membrane. The main difference between the RO and UF is that RO has smaller holes compared to UF. That’s why you need a pressure pump to drive the water through RO membranes. The UF membrane must be changed after a certain period of time as the pollutants can block the holes.
UV(Ultra Violet) technology
Ultraviolet light is harmful for living organisms. Staying in UV light for a prolonged time is very harmful to us. But, we can use it to remove bacteria and viruses from water. It does not have the capability to remove Arsenic or Fluoride from water. It can only remove bacteria and viruses from water using germicidal UV light. The extra advantage of UV technology is that it does not waste water.
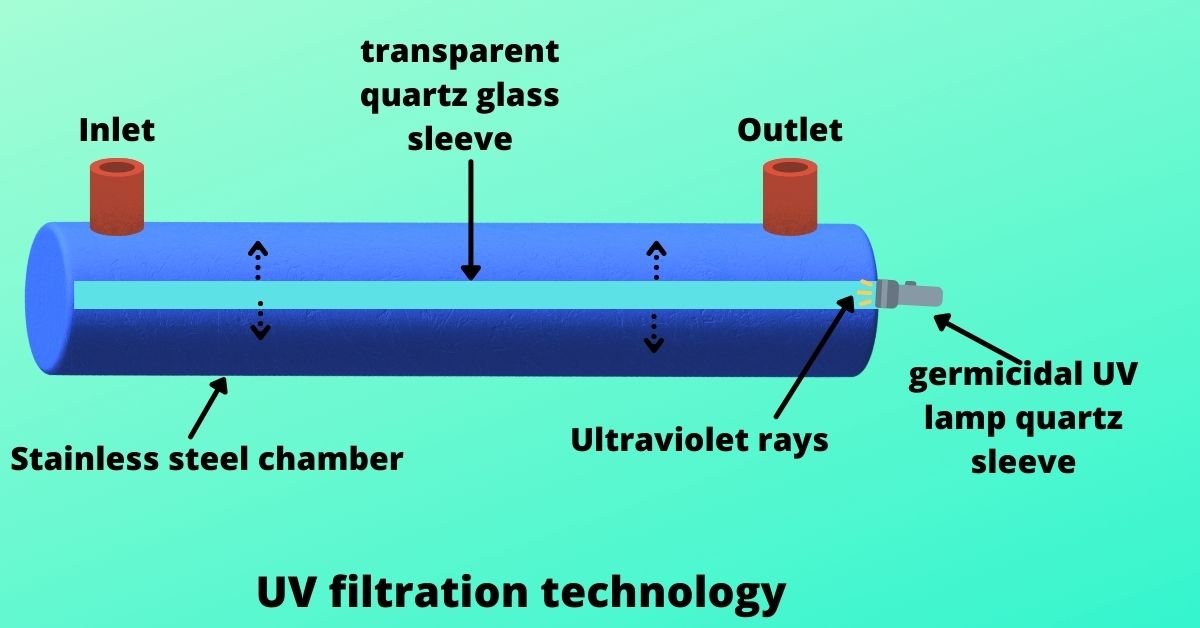
In UV technology, water passes through a stainless steel container. A transparent glass quartz sleeve holds the UV lamp. As UV lamps use electricity it is better to isolate the lamps from water. The sleeve is made transparent because UV light can penetrate the transparent glass. So all the harmful bacteria and viruses are killed by the UV light. To keep the mechanism running, you will need to have a constant power supply.
Besides RO and UF you can consider distillation, ion exchange to remove arsenic.
Government approach
The Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation provides a Centrally Sponsored Scheme, the National Rural Drinking Water Programme (NRDWP). It was restructured as Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) to provide Functional Household Tap Connection (FHTC) to every rural household i.e Har Ghar Jal, by 2024. Along with this, under JJM, a pilot survey was introduced in 10 cities i.e. Agra, Badlapur, Bhubaneswar, Churu, Kochi, Madurai, Patiala, Rohtak, Surat and Tumkur by the Government of India. Face to face interviews, call interviews, water sample testing, lab testing etc. will be conducted under this survey.
Conclusion
It is very much clear that the water crisis will be a serious concern like global warming. Helping to get safe drinking water for everyone is the main motive of this topic. Please stop wasting water and share this article as much as you can.

If you find something unusual in your home water, try to do a lab test as soon as possible and inform your local authorities. Always use a water purifier if you are not sure about the source of that water. At least use the TDS level of the water to select your water purifier.
In the end, the drinking water crisis is becoming a global pandemic day by day. It is a collective approach that also should be done at individual levels. Take safe water and try to avail the minimum safe water standards to those who are not concerning or do not have the Affordability to take it.
That’s it for this post. If you have any query please feel free to comment below. Thank you.
Reference
- “Membranes for Water Treatment: Reverse Osmosis and Nanofiltration”- the University of Texas at Austin (https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&url=https://www.twdb.texas.gov/publications/reports/numbered_reports/doc/r363/c6.pdf&ved=2ahUKEwiP_fvw3P3xAhVTU30KHd_0An4QFjAOegQIHBAF&usg=AOvVaw1qJkBWtpSKZ0rPj2F4WdBQ)
- Total dissolved solids in Drinking-water – WHO | World Health Organization (https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&url=https://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/chemicals/tds.pdf&ved=2ahUKEwj08aWyjYvyAhXqxzgGHfApBFQQFjALegQIHxAC&usg=AOvVaw3Jlni0keSfGm1ZD2kMGxTg)
- Children and Adolescents in Urban India – NIUA(https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&url=https://niua.org/intranet/sites/default/files/702.pdf&ved=2ahUKEwit2_6P14zyAhUczjgGHdLNBesQFjAAegQIBRAC&usg=AOvVaw0rQpf3P9xfG4-FcSHEavv-)
- Colour, taste and odor problems in drinking water-(https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&url=https://www.doh.wa.gov/portals/1/Documents/pubs/331-286.pdf&ved=2ahUKEwjJvZC_s6jyAhXzqpUCHbceDuAQFnoECAQQBg&sqi=2&usg=AOvVaw0PAMgY6oZHIVZdqnD5k385)
- Clean drinking water-(https://www.unicef.org/india/what-we-do/clean-drinking-water)
- Jal Jeevan Mission-(https://jalshakti-ddws.gov.in/)
- India’s water and sanitation crisis-(https://water.org/our-impact/where-we-work/india/)
- Health impact of supplying safe drinking water containing fluoride below permissible level on fluorosis patients in a fluoride-endemic rural area of West Bengal-(https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22298140/)
- Fluoride- (https://www.indiawaterportal.org/topics/fluoride)
- Arsenic Contamination of Groundwater: A Review of Sources, Prevalence, Health Risks, and Strategies for Mitigation-(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4211162/)
- Government launches pilot survey on drinking water in 10 cities-(https://www.newindianexpress.com/nation/2021/feb/17/government-launches-pilot-survey-on-drinking-water-in-10-cities-2265086.html)
- Water Quality Parameters and BIS standards for various chemical and biological constituents- (http://iitk.ac.in/iwd/wq/drinkingwater.htm)
What is Tds?
Total dissolved solids (TDS) is a measure of all inorganic and organic substances present in a liquid in molecular, ionized, or micro-granular (colloidal sol) suspended form.
Which technology should I use to remove Arsenic from water?
RO or UF.

