Taxonomy is a very important branch of biology which deals with the classification of living organisms. This word was first used by Augustin P. de Candole who lived during the 18th century and also developed taxonomic hierarchy.
Taxonomy, originating from two Greek words ‘taxis’ means arrangements and ‘nomos‘ means method.
Systematics is the study of internal relationships, classification and diversities of living organisms. Taxonomy is often referred as the synonym of systematics.
Components of taxonomy
Identification
It is the step of identifying an organism from the others by using some specific characters.
Characterization
It is the study of all morphological and anatomical characteristics of the newly found organism.
Classification
It is the process of assigning various ranks in the hierarchy of classification and based on phylogeny and phenotype.
Nomenclature
It is the process of giving scientific names to an organism and it is the application of formal rules for naming organisms.
The relation between Taxonomy and systematics
Both taxonomy and systematics study the diversification, internal and external relationships among living organisms. Both are involved in characterizing organisms by the use of morphological, behavioural, genetics and biochemical observations.
But according to scientist Mason, taxonomy is related to description, identification, classification and naming of plants and animals, whereas systematics is only related to classification.
Scientists Lam and Tuwill (1964) used these two as synonymous words.
Hierarchical classification
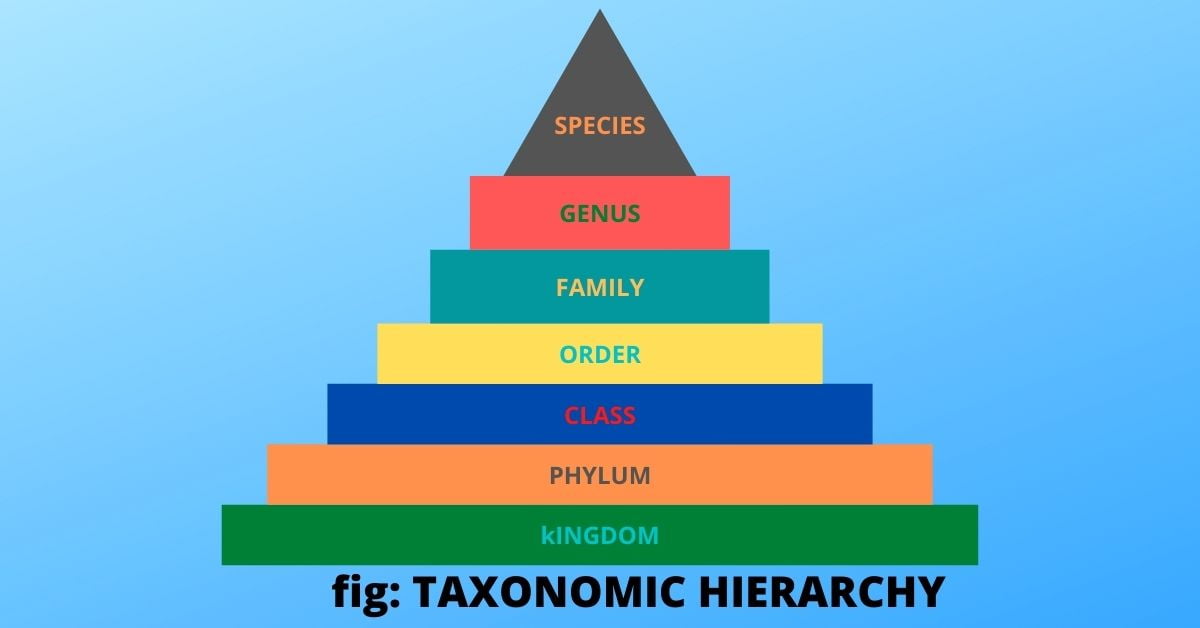
All living organisms are classified into different levels or groups on the basis of their some important characteristics. But their appearance, reproduction, mobility and functionality are few ways in which organisms are grouped together. Within each group, they are further divided into smaller groups. This grouping system makes it easier for many scientists to study a certain group of organisms. These specialized groups are collectively called Hierarchical classification of living things.
This classification includes 7 levels such as-
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species.
Kingdom
The most basic classification of living organisms is the kingdom and it is the highest taxonomic level. They placed into this kingdom on how they obtain their food, the types of cells that can make up the body and the number of cells they contain. Living organisms divided into 5 kingdoms i.e. monera, Protista, Plantae, fungi, animalia.
Phylum
It is the next level in the classification and more specific than the kingdom. It is an important step to find some kind of physical or morphological similarities among organisms within a kingdom. These similarities suggest that there is a common ancestry among those organisms in a particular phylum.
There are 35 phyla in animalia kingdom such as Chordata, Porifera, Anthropoda etc.
Classes
Classes are the most general rank until phyla were not introduced. Organisms of a class have been more in common than those in an entire phylum. Total of 108 classes present in kingdom Animalia including class mammalia, reptilia, aves etc.
Order
Organisms in each class are further divided into orders. Order is a more specific rank than class. This is used to determine which order an organism belongs. A taxonomic key is nothing more than a checklist of characteristics that determines how organisms are grouped together.
Family
Orders are divided into many families. Organisms within a family have more in common that organisms in any classification level above it. Because they share many characteristics that are in common with other organisms of a family that are said to be related to each other.
Genus
Genus is a step to describe the generic epithet for an organism. Genus is more specific than other classifications so there are fewer organisms within each one. For this reason, there are a lot of different genera along with both plants and animals. When using the taxonomy to name an organism, the genus is used to determine the first part of its part name.
Species
It is the lowest and most important level of classification of living things. The species part of an organism determines the second part of its two-part name. It refers to a group of organisms that are similar in shape, formation, anatomical and reproductive features. Total of 8.7 million different species found in the whole world. Next species is also divided into subspecies levels.
Taxonomic hierarchy
A taxon (plural: taxa) is a group of organisms that are classified as a unit. Taxonomic hierarchy is the process of arranging various levels of organisms into successive levels of the biological classification either in an increasing manner or decreasing manner of order from kingdom to species and also in vice versa form. Each level of the hierarchy is called the taxonomic category or rank.
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Importance of taxonomy
- Millions of organisms are classified scientifically into different categories by the process of taxonomic classification which helps to a better understanding.
- It helps to ascertain the number of living organisms in the world. More than one million species of plants and animals have been discovered and classified by the help of taxonomic knowledge.
- It gives an idea of the order of physical development.
- To indicate the distribution and habitat of plants and animals on earth and their benefits over the environment.
- It gives an idea of local fauna and flora thus helping us to distinguish the endemic species.
- To indicate the source and genetic relationships (phylogenetic), ancestry, and origin of plants.
- Different types of application in applied biology such as agriculture, public health and environmental biology depend on the classification of taxonomy.
What is taxonomy?
Taxonomy is a very important branch of biology which deals with the classification of living organism.
What is systematics?
Systematics is the study of internal relationships, classification and diversities of living organisms. Taxonomy is often referred as the synonym of systematics.
What are the hierarchical classification of taxonomy?
This classification includes 7 levels such as- Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species.
Who coined the word “Taxonomy”?
This word was first used by Augustin P. de Candole who lived during the 18th century and also developed taxonomic hierarchy.

