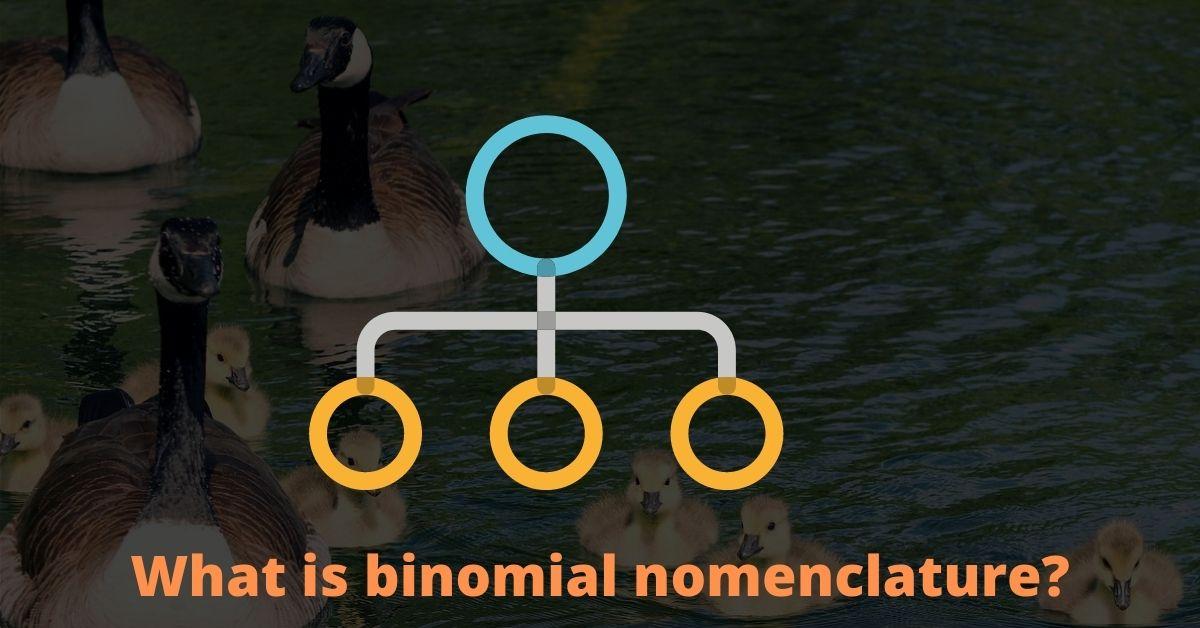
It is a naming system in taxonomy, which is composed of two terms. The first term indicates the Generic epithet and the second term indicates the Specific epithet of any organism.
What is binomial nomenclature?
Each and every organism has different local names in different localities. These multiple local names make a difficult situation to identify a specific organism globally and keep a track of the number of species. So, it creates a lot of confusing matters.
To overcome this problem, Carolus Linnaeus introduced this naming procedure called ‘Binary Nomenclature’ or ‘Binomial Nomenclature’. He first introduced this system in his writing ‘Species Plantarum‘(1753) and next also mentioned it in ‘Systema Naturae‘(1758). This is a formal naming system composed of two parts both of which use Latin grammatical forms. By this system, a standard naming protocol came up. According to it each and every living organism has one specific scientific name which is used by everyone to identify this specific kind of organism.
Rules of binomial nomenclature
The application of this system is now mainly governed by two International codes that are International code of zoological nomenclature (ICZN) for animals and International code of botanical nomenclature (ICBN) for algae, fungi and plants. A biologist from all over the world follows these unique set of procedures forbinomial nomenclature –
- Scientific names must be written in Italics or this line must be underlined when handwritten.
- There are two parts: one is a generic epithet and the other is a specific epithet.
- The generic epithet is always written first.
- The genus name must be capitalist.
- The species name is not capitalist.
- If any plant and animal have many scientific names then according to the law of priority which name is given at first that will be valid.
- For valid publication of a scientific name, at first, this name will be introduced in some important science journal.
Methods of Naming of Genus and Species
Genus
Genus is a uninominal singular word which is treated as a noun and first letter written in capital form. The genus may have masculine, feminine, and neuter gender and for this different formation, the genus name ends with several suffixes. For masculine gender used us( Catharanthus) or pogon( polypogon) and for feminine gender used a(rosa) or is(iris) and used um(Lycopodium) for neuter gender.
The naming process-based under these –
- Commemoration of a person :
Commonly an author such as Bauhinia for Bauhin, Benthamia and Benthamida for Bentham, Darwinia for Darwin, Hutchinsonian for Hutchinson, Linnaea for Linnaeus. It may also be used for the head of a state such as Victoria for Queen Victoria of England,
- Based upon important character :
Such as Hygrophila for its marshy habit, Acanthosperm for spiny fruit, Hepatica for its liver like leaves, Trifolium for its trifoliate leaves etc.
- Based on place :
Such as Araucaria depends on Arauco province of Chile, Arabis for Arabia, Sibiraea for Siberia. It also depends on two places together, such as Austro Americium ( Australia and America).
- Basis of aboriginal name :
Gingo which is a Chinese language, vanda a Sanskrit and Sasa a Japanese aboriginal name.
- Based on mythological name :
Such as Nymphaea based on God of water or Nymph.
Species
The full name of species is binomial consisting of two terms, first is generic epithet followed by specific epithet that is always small in letter and this is always used after the genus form. A specific epithet is commonly derived from these sources –
- Name of a person :
Iris hookeri ( based on Hooker) and Indigofera linnaei ( based on Linnaeus)
- Basis of place :
Ficus bengalensis found mainly in Bengal, Solanum Indicum mainly found in Indian areas.
- Based on characters :
A name based on a white plant part may take the form alba (Rosa alba), album (chenopodium album), Albus ( Mallotus albus) depending on the gender of the genus to which the epithet is assigned.
- The noun in apposition :
A specific epithet may sometimes be a noun in apposition carrying its own gender. Binominal Pyrus malus based on the Greek name malus for common apple. In Allium cepa, cepa is the Latin name for onion.
Trinomial classification
It refers to names for taxa below the rank of species. There are three parts to this classification. It has different uses in botany and zoology.
In Zoology, animals are given scientific names that are governed by ICZN. Only one rank is allowed below the rank of species that are called Subspecies. Buteo jamaicensis borealis is one example of the subspecies.
In Botany below the species, rank is variety and forma and more ranks can be made by using the prefix ‘sub’ to make subspecies, subvariety and subforma. Example, Corylopsis sinensis var. Calvescens f. Veitchiana is an ornamental type of plant.
what do you mean by binomial nomenclature?
It is a naming system in taxonomy, which is composed of two terms. The first term indicates the Generic epithet and the second term indicates the Specific epithet of any organism.
how many factors comes under the naming of genus of Binomial Nomenclature?
Five.
how many factors comes under the naming of species of Binomial Nomenclature?
Four.
what is Trinomial Nomenclature?
It refers to names for taxa below the rank of species. There are three parts to this classification. It has different uses in botany and zoology.