Biology is the natural science, focusing on the study of life and living organisms and also for non-living organisms. It includes the organism’s nature of origin, physiological mechanisms, chemical structure, molecular interaction that causes growth and development next to their adaptation & evolution due to environmental change.
Introduction
It is a combined word made from two Greek words ‘ bios‘(life) &’ logos‘(study). It comprises the cytological analysis of living things, the energy metabolism that underlies the activities of life and genetic basis for inheritance in organisms. This defined the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity and evolution as the engine that propels the creation & extinction of species. In 1801, Lamarck 1st proposed the word’ Biology‘.

History of Biology
About 3.7billion years ago simple living objects created from through multiple chemical reactions and procedures. After that all simple molecules transformed into complex molecules through the process of Polymerization technique – that is carbohydrate, protein, lipid, amino acid, fatty acid, nucleic acid etc. Next, all these molecules create the first living cell. This type of cell is prokaryotic, example -bacteria, blue-green algae etc. After that prokaryotic cell form eukaryotic type of cell that more advance from the previous one. Plant and animal cell originates from these eukaryotic type of cell.
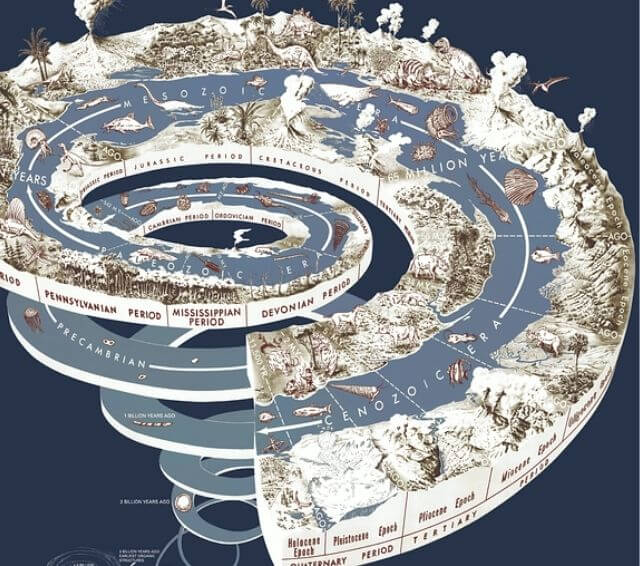
This science describes the study of the whole world from ancient to modern times. Biology began many many years ago, that is Egyptians having advanced knowledge about the human body around 2800BC that is 5000 years ago. The first person who gave a great contribution in biology is Alcmaeon, who lived in Crotona in the 5th century, first practised dissection in his research. Crotona is famous at that time for its Pythagorean scholars.
Later Aristotle is considered to be the first to practice scientific zoology. He performed extensive studies on marine life & plants. He is known as ‘Father of Zoology‘. His student, Theophrastus, wrote the botanical text in 300B.C. on the structure, life cycle and use of plants. He is known as ‘Father of Botany‘.
In the 8-15th century, Leonardo da Vinci participated in human dissection and making detailed anatomical drawings. One of the first illustrated biology books written by German botanist Leonhard Fuchs in 1542. Next in 1665, Robert Hooke used a simple microscope to examine a thin slice of cork, from which he observed that plant tissue consists of rectangular units which he called ‘cell‘. In 1676, Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek published the first drawing of living single-celled organisms.
During the 19th century, thousands of new specimens were discovered. In 1859, Charles Darwin published ‘On the origin of species’, that text showing all living organisms are interrelated, they are not separately created they are separated due to adaptation and evolution.
The 20th & 21st century known as ”Biological Revolution”. Mendel is known as “Father of Genetics“ for his discovery about Gene. Later Watson and Crick explained the molecular & chemical structure and function of DNA in 1953. In the late 20th century new fields like Genomics and Proteomics were described. Finally, the Human genome project was launched in 1990 with the goal of mapping the general human genome and completed in 2003. These are the steps to incorporate and accumulate knowledge of biology for the development of the whole world.
Branches & Career options
Biology is the vast area of science with a variety of subdivisions that all are concerned about aspects of ancient to modern life. There are countless career opportunities ranging from basic science to agricultural and industrial application.
The major branches –
- Botany – branch of science that deals with the study of plants.
- Zoology – this is the branch of science which deals with the description and distribution of animals.
- Microbiology – deals with the study of micro-organisms.
i) Branches of pure biology
- Cytology –the study of formation, structure, molecular interactions occur within a living cell.
- Morphology -the total general structure that is external form, size, shape, colour, other features of living beings.
- Anatomy – description of organisms internal structure.
- Histology – the study of tissue systems.
- Embryology – the study of development means fertilization, growth, division of the zygote into the embryo.
- Genetics – the study of inheritance of genes and heredity.
- Ecology – the study of interactions between living and nonliving elements.
- Taxonomy – this is the science of description, identification, nomenclature and classification of organisms.
- Pathology – the study of various diseases in plants and human beings.
- Osteology – the study of structure and function of skeleton and bone structure.
- Agroforestry – this branch deals with the form of land where herbaceous crops are cultivated.
- Evolution – deals with internal relationships between organisms of past and present days.
ii) Branches of applied biology
Applied botany
- Agriculture – the cultivation of food and fibre yielding plants.
- Horticulture – the study of flowering and fruiting plants.
- Pharmacology – the study of interactions between drugs and organisms.
- Plant breeding – It is a purposeful manipulation of plant species for creating desired genotypes and phenotypes.
- Cryobiology – effects on life at a very lower temperature.
- Palynology – study about pollen grains.
- Pharmacognosy – dealing about medicinal plants.
- Phycology – study about algae.
- Mycology – the study of fungal elements.
- Pteridology – study about pteridophyte.
- Bryology – study about bryophytes.
- Dendrology – the study of herbs and trees.
Applied Zoology
- Pisciculture – the study of rearing of fishes.
- Sericulture – silk industry forms the culture of silk moths.
- Apiculture – the study of beekeeping.
- Poultry – the study which deals with keepings of the foul.
- Angiology – science deals with the study of the blood vascular system.
- Parasitology – the study of parasites and parasitism.
- Entomology – the study of insects.
- Ornithology – the study of birds.
- Malacology – the study of molluscs.
- Immunology – the study of resistance capacity against different diseases.
- Dermatology – the study of skins.
- Serology – the study of serum, interactions between antigen and antibody in the blood.
iii) Branches of modern biology
- Molecular Biology – the study of the physicochemical organization, interaction of biomolecules that control activities of protoplasm.
- Biotechnology – use of biological organisms in commercial production such as drugs, vaccines and hormones.
- Genetic engineering – direct manipulation of genes using biotechnology.
- Ethnobotany – the importance of medicinal plants near rural people.
- Floriculture – the study of flowering plants.
- Silviculture – study of the development of forests.
- Olericulture – study about vegetables yielding plants.
- Cardiology – study about functions of the heart.
- Forensic science – use of biological data to criminal investigation and legal problems.
- Astrobiology – concerned about the origin, adaptation, evolution, distribution and future of life in the universe.
- Gynaecology – the study of female reproductive organs.
- Neurology – study about the nervous system.
- Oncology – the study of cancer.
- Euphenics – improvement of the human race by medical engineering or genetic disorder.
- Eugenics – improvement of the genetic race by applying laws of heredity. This technique applied before birth.
- Euthenics – improvement of the human race by improving environmental conditions. It applied after birth.
Relationship with other branches of Science
- Biophysics – the study of biological procedures by applying the sequence and methods employed in physical science.
- Biochemistry – the study of chemical reactions which is important for the creation and existence of life.
- Biogeography – description and distribution of species according to their geographical position.
- Palaeontology – the study of fossils and geographical evidence of prehistoric ages.
- Bionics – combined study together with biology and electronics.
- Biometry – the application of statistical analysis into biological data.
- Anthropology – the branch of sociology which deals with the source of origin, distribution, development, relationship and culture of human bodies.
- Cybernetics – the scientific and disciplinary application for describing regulatory systems, their structure, constraints and possibilities.
- Bioinformatics – the use of information technology for study the procedure, collection and storage of genomic, proteomics and all other biological data.
- Psychology – mental ability and characteristics of the human mind.
If you have any query regarding this post please comment below. We will try our best to answer. Thank you.
what is biology?
Biology is the natural science, focusing on the study of life and living organisms and also for non-living organisms. It includes the organism’s nature of origin, physiological mechanisms, chemical structure, molecular interaction that causes growth and development next to their adaptation & evolution due to environmental change.
who is the father of “zoology”?
who is the father of “botany”?
who proposed the word’ Biology‘?
In 1801, Lamarck 1st proposed the word’ Biology‘.
who is known as “Father of Genetics“?

